A Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT) is an automatic transmission that uses a belt and pulley system to continuously vary the gear ratio. There are no fixed gears, allowing for a smooth transition between different gear ratios.
Unlike traditional gearboxes that use a series of fixed gears, CVTs offer a wider range of gear ratios, providing a more efficient and comfortable driving experience. This makes CVTs particularly suitable for car rental companies, as they can offer a more enjoyable and fuel-efficient experience for their customers.
How CVTs Work
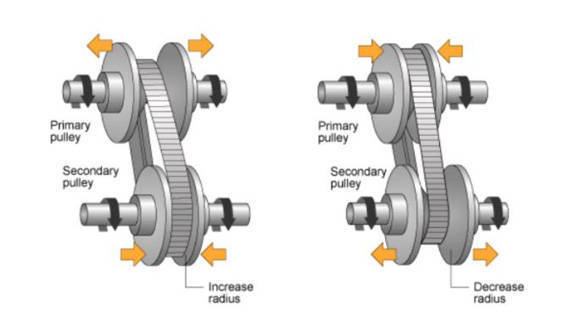
CVTs consist of two pulleys connected by a belt. One pulley has a larger diameter, while the other has a smaller diameter. As the belt moves between the pulleys, the effective gear ratio changes. This allows the CVT to continuously adjust the gear ratio to match the engine speed to the vehicle’s speed.
Hydraulic pressure controls the movement of the pulleys. By adjusting the hydraulic pressure, the CVT can change the effective gear ratio, providing a smooth transition between different speeds.
Advantages of CVTs
- Improved Fuel Efficiency: CVTs can help improve fuel efficiency by selecting the optimal gear ratio for different driving conditions. This can lead to better fuel economy, especially in highway driving.
- Smoother Shifting Experience: CVTs offer a smoother shifting experience compared to traditional gearboxes. This is because there are no discernible gear shifts, resulting in a more comfortable ride.
- Reduced Noise and Vibration: CVTs can help reduce noise and vibration, providing a quieter and more refined driving experience.
- Increased Acceleration: CVTs can provide a more responsive acceleration experience, especially in lower gear ratios. This can make it easier to accelerate quickly when needed.
- Versatility: CVTs are versatile and can be used in a variety of vehicle types, including cars, SUVs, and even hybrid vehicles.
Disadvantages of CVTs
While CVTs offer several advantages, there are also some potential drawbacks:
- Durability: CVTs can be less durable than traditional gearboxes, especially when subjected to heavy towing or off-road use.
- Performance Perception: Some drivers may find the continuous shifting of a CVT to be less engaging or sporty compared to the distinct gear shifts of a traditional gearbox.
- Cost: CVTs can be more expensive to repair or replace compared to traditional gearboxes.
Types of CVTs
There are three main types of CVTs:
1. Toroidal CVTs
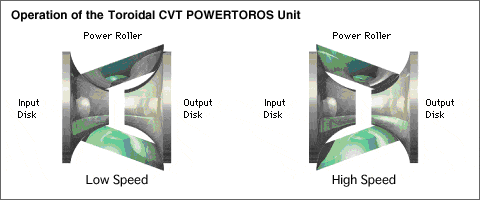
- Description: Toroidal CVTs utilise a toroidal-shaped pulley and a push belt. The belt is pressed against the outer edge of the pulley, causing it to expand or contract, effectively changing the gear ratio.
- Function: These CVTs utilise a unique toroidal pulley, shaped like a doughnut with a central hole and an outer rim. A specialised push belt presses against the outer edge of this pulley.
- Gear Ratio Change: As the hydraulic pressure controls the movement of the push belt, it compresses or expands against the toroidal pulley. This changing contact area between the belt and pulley effectively varies the gear ratio.
- Benefits:
- Compact Size: The toroidal design allows for a smaller overall transmission unit, making it ideal for space-constrained applications.
- High Efficiency: Due to the minimised friction between the belt and pulley, toroidal CVTs are known for their excellent fuel efficiency.
- Drawbacks:
- Limited Torque Capacity: The pushing action of the belt may limit the maximum torque these CVTs can handle, making them less suitable for high-performance vehicles.
- Complexity: The unique design can be more complex to manufacture compared to other types.
2. Push-belt CVTs

- Description: Push-belt CVTs use two conical pulleys connected by a push belt. The belt is pushed against the conical surfaces of the pulleys, varying the effective gear ratio.
- Function: These CVTs employ two conical pulleys connected by a push belt. The base of each cone connects to a shaft.
- Gear Ratio Change: Similar to toroidal CVTs, hydraulic pressure controls the push belt. As the belt moves between the conical surfaces, it pushes them apart or squeezes them together, changing the effective gear ratio.
- Benefits:
- Versatility: The simple and adaptable design allows for use in a wide range of vehicles and driving conditions.
- Reliability: Push-belt CVTs are known for their robust design and reliable performance.
- Drawbacks:
- Larger Size: The conical pulleys can be bulkier compared to toroidal designs.
- Potential for Efficiency Loss: Friction between the belt and conical surfaces may be slightly higher than in toroidal CVTs, impacting fuel efficiency to some extent.
3. Hybrid CVTs:

- Description: Hybrid CVTs combine elements of both toroidal and push-belt CVTs, often incorporating a combination of toroidal and conical pulleys.
- Function: These CVTs, as the name suggests, combine elements of both toroidal and push-belt designs. This can involve using a combination of toroidal and conical pulleys or a hybrid belt design.
- Gear Ratio Change: The specific mechanism for changing the gear ratio depends on the manufacturer’s design. It may involve a combination of the push-belt and toroidal methods described above.
- Benefits:
- Balance of Advantages: Hybrid CVTs aim to strike a balance between the efficiency benefits of toroidal designs and the durability and versatility of push-belt systems. They can offer good fuel economy, a compact size, and reliable performance.
- Drawbacks:
- Complexity: The combined design elements can make them slightly more complex to manufacture compared to simpler push-belt CVTs.
Remember:
- The specific design and components of CVTs can vary depending on the manufacturer and application. These descriptions provide a general understanding.
- While each type offers advantages, the optimal choice depends on factors like vehicle type, power requirements, and desired driving experience.
By understanding these details, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the innovative world of CVT technology and its role in modern vehicles.
CVTs in Electric Vehicles
CVTs are becoming increasingly popular in electric vehicles (EVs) due to several advantages:
- Efficiency: CVTs can optimize the efficiency of an electric motor by continuously adjusting the gear ratio to match the vehicle’s speed and the motor’s operating range.
- Smooth Acceleration: CVTs provide a smooth and linear acceleration experience, which is often preferred in EVs.
- Regenerative Braking: CVTs can be integrated with regenerative braking systems to capture kinetic energy and convert it into electricity, improving the vehicle’s range.
- Compact Size: CVTs are generally smaller and lighter than traditional gearboxes, making them well-suited for electric vehicles.
Maintenance and Care for CVT Vehicles
Regular Maintenance
While CVTs are generally low-maintenance transmissions, it’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Fluid Changes: Regularly replace the CVT fluid according to the manufacturer’s specifications. This is crucial for maintaining the transmission’s proper operation and preventing wear and tear.
- Inspection: Have your vehicle’s CVT inspected by a qualified mechanic at recommended intervals. This includes checking for fluid leaks, unusual noises, or signs of overheating.
- Belts and Pulleys: Inspect the CVT’s belt and pulleys for signs of wear or damage. Replace them if necessary to prevent transmission failure.
Specific Considerations
- Driving Habits: Aggressive driving, heavy towing, or frequent stop-and-go traffic can put extra strain on a CVT. Avoid excessive wear and tear by driving smoothly and avoiding harsh acceleration or braking.
- Overheating: Overheating can be detrimental to a CVT. Avoid prolonged idling or driving in extreme conditions that could cause the transmission to overheat.
- Towing: While some CVTs are designed for towing, it’s important to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual to determine its towing capacity and limitations. Exceeding the towing capacity can strain the CVT and lead to premature wear.
CVTs and Towing
Towing Capacity and Limitations
- Manufacturer’s Guidelines: Always refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific towing capacity information.
- Weight Restrictions: CVTs may have limitations on the weight of trailers they can tow. Exceeding these limits can damage the transmission.
- Trailer Braking: Ensure that your trailer has adequate brakes to control its speed and prevent excessive strain on the CVT.
Safety Considerations
- Proper Hitch Installation: A properly installed hitch is essential for safe towing. Consult a professional for installation if needed.
- Weight Distribution: Distribute the weight of the trailer evenly to avoid overloading the vehicle’s rear axle.
- Driving Techniques: Adjust your driving style to accommodate the added weight of the trailer. Avoid sudden acceleration, braking, or turning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about CVTs
-
Are CVTs more expensive to maintain than traditional gearboxes?
- While CVTs can require specific maintenance, such as regular fluid changes and inspections, their overall maintenance costs are comparable to traditional gearboxes.
-
Can I tow with a CVT vehicle?
- Yes, many CVT vehicles are equipped for towing. However, it’s crucial to consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific towing capacity and limitations.
-
Are CVTs as durable as traditional gearboxes?
- CVTs have improved significantly in terms of durability over the years. However, they can still be more sensitive to harsh driving conditions or overloading compared to traditional gearboxes.
-
Is a CVT better than a traditional gearbox?
- The choice between a CVT and a traditional gearbox depends on your driving needs and preferences. CVTs offer smoother shifting, improved fuel efficiency, and can be more suitable for certain applications, while traditional gearboxes may provide a more engaging driving experience for some.
-
Can I feel the gear shifts in a CVT?
- Unlike traditional gearboxes, CVTs do not have distinct gear shifts. The transition between gear ratios is smooth and seamless.
-
Is it okay to drive a CVT vehicle in stop-and-go traffic?
- While CVTs are designed to handle stop-and-go traffic, excessive idling or frequent stops can put extra strain on the transmission. It’s advisable to avoid prolonged idling and abrupt starts and stops.
-
Can I use a CVT vehicle for off-roading?
- Some CVTs are designed for off-road use, but it’s essential to check your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific limitations and recommendations. Excessive off-roading can put a strain on the CVT.
-
What are the signs of a failing CVT?
- Signs of a failing CVT can include unusual noises, slipping gears, or a burning smell. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to have your vehicle inspected by a mechanic.
-
Can I install a CVT in my existing vehicle?
- Converting a vehicle from a traditional gearbox to a CVT is generally not feasible. The design and engineering of the vehicle would need to be significantly modified.
-
Are CVTs suitable for high-performance vehicles?
- While CVTs can be used in high-performance vehicles, they may not provide the same level of engagement and direct control as traditional gearboxes. For enthusiasts seeking a more sporty driving experience, a traditional gearbox might be a better option.
Additional Resources
- Automotive Websites:
- Edmunds: https://www.edmunds.com/
- Kelley Blue Book: https://www.kbb.com/
- Car and Driver: https://www.caranddriver.com/
- Forums:
- Reddit: r/askcars
- Car Talk: https://www.npr.org/podcasts/510208/car-talk
- NHTSA: https://www.nhtsa.gov/
