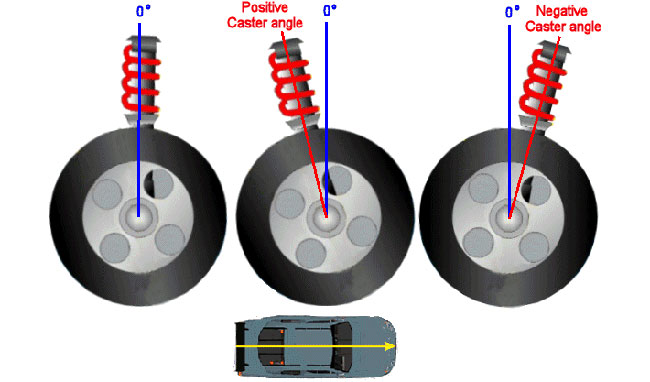
Caster angle refers to the forward or backward tilt of the steering axis when viewed from the side of the vehicle. It’s a crucial factor in vehicle handling and steering feel.
Types of Caster Angles
Positive Caster:
- The top of the steering knuckle is positioned forward of the bottom, creating a forward-leaning angle.
- Benefits:
- Self-centering Steering: A positive caster causes the steering wheel to naturally return to the centre position after a turn, reducing driver effort.
- Improved High-Speed Stability: Positive caster enhances straight-line stability, especially at higher speeds.
- Drawbacks:
- Heavier Steering: A positive caster can make steering feel heavier, particularly at low speeds.
Negative Caster:
- The top of the steering knuckle is positioned backward from the bottom, creating a backward-leaning angle.
- Benefits:
- Lighter Steering: A negative caster can make steering feel lighter and more responsive.
- Improved Turn-In Response: It can enhance a vehicle’s turn-in response, making it more agile.
- Drawbacks:
- Reduced Straight-Line Stability: Excessive negative caster can lead to reduced straight-line stability and a tendency to wander.
- Increased Tyre Wear: A negative camber can accelerate tyre wear, especially on the inner edges.
How Caster Works: A Deeper Dive
A caster angle is a critical suspension geometry setting that significantly impacts a vehicle’s handling and steering feel. To understand how it works, let’s visualize a shopping cart:
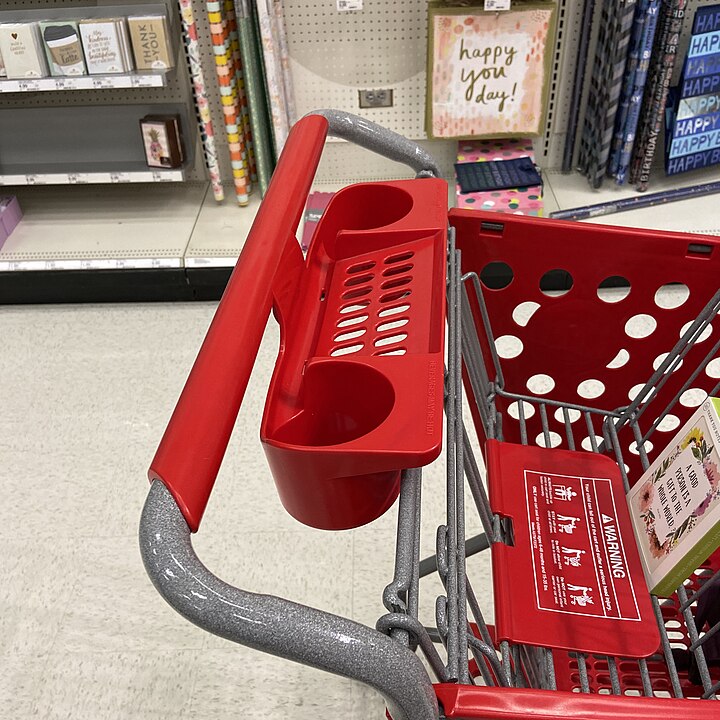

Notice how the steering axis leans forward, creating a self-centering effect. When you turn the handle, the wheels turn, and as you release the handle, the wheels naturally return to the straight-ahead position. This self-centering action is due to the positive caster angle.
- Self-Centring Effect: When you turn the steering wheel and then release it, the positive caster angle causes the wheels to naturally return to the straight-ahead position.
- Improved Straight-Line Stability: A positive caster enhances the vehicle’s stability at higher speeds by resisting forces that could cause the steering wheel to wander.
- Increased Steering Effort: A more positive caster can result in heavier steering, especially at low speeds.
Negative Caster Angle:
While positive caster is common in most vehicles, negative caster can be used in certain applications, such as racing cars, to improve responsiveness and turn-in. However, excessive negative caster can lead to reduced stability and increased tyre wear.
In summary:
- Positive Caster: Improves stability, and reduces steering effort at higher speeds.
- Negative Caster: Improves responsiveness and turn-in, but can reduce stability at higher speeds.
The optimal caster angle for a vehicle depends on various factors, including vehicle type, tyre size, and suspension geometry. A well-tuned suspension system with the correct caster angle can significantly enhance a vehicle’s handling and driving experience.
Impact of Caster Angle on Vehicle Performance
Caster angle plays a significant role in influencing a vehicle’s handling characteristics and overall performance. Here’s a breakdown of its effects:
Steering Feel and Responsiveness
- Positive Caster:
- Heavier Steering: A positive caster can make steering feel heavier, especially at low speeds.
- Improved Steering Return: It enhances the self-centering tendency of the steering wheel, making it easier to maintain a straight course.
- Negative Caster:
- Lighter Steering: A negative caster can make steering feel lighter and more responsive, particularly at low speeds.
- Quicker Turn-in: It can improve a vehicle’s turn-in response, making it more agile.
Straight-Line Stability
- Positive Caster: Positive caster enhances straight-line stability, especially at higher speeds, by resisting forces that could cause the steering wheel to wander.
- Negative Caster: Excessive negative caster can reduce straight-line stability, making the vehicle more prone to wandering or darting.
Cornering Ability
- Both Positive and Negative Caster: Both positive and negative caster can influence cornering ability.
- Optimal Camber Angle: The optimal camber angle for cornering depends on various factors, including tyre compound, suspension geometry, and driving style.
- Tyre Wear: Excessive camber angle, whether positive or negative, can lead to uneven tyre wear, reducing tyre life and affecting vehicle performance.
Factors Affecting Caster Angle
Several factors influence the optimal caster angle for a vehicle:
- Suspension Geometry: The design of the suspension system, including the steering knuckle and control arm angles, determines the vehicle’s caster angle.
- Tyre Size and Type: Different tyre sizes and types can affect the effective caster angle.
- Vehicle Weight Distribution: The weight distribution of the vehicle can influence the impact of the caster angle on handling and stability.
- Driving Conditions: Road conditions, such as uneven surfaces or potholes, can affect the actual caster angle experienced by the vehicle.
Adjusting Caster Angle
Professional Alignment
For most vehicles, adjusting the caster angle requires specialised equipment and expertise. It’s best to have a professional mechanic perform a wheel alignment to ensure proper settings. A wheel alignment will check and adjust caster, camber, and toe angles to optimise vehicle performance and tyre wear.
DIY Adjustments (if applicable)
While some vehicles, especially older models or those with adjustable suspension systems, may allow for minor caster angle adjustments, it’s generally not recommended for DIY enthusiasts. Incorrect adjustments can negatively impact vehicle handling, safety, and tyre wear.
Caster Angle in Racing
In motorsports, caster angle is a crucial factor in vehicle setup. Racers often use extreme caster angles to optimise performance for specific track conditions and driving styles.
Tuning for Optimal Performance:
- Track Conditions: Different track conditions, such as high-speed circuits or technical tracks, require different caster angle settings.
- Tyre Compound: The type of tyre compound used can also influence the optimal caster angle.
- Driver Preference: Driver preference and driving style can also play a role in determining the ideal caster angle.
By carefully tuning the caster angle, race car drivers can achieve optimal handling and performance.
FAQs about Caster Angle
1. What is the ideal caster angle for street driving?
A slight amount of positive caster angle is typically ideal for street driving. This helps with straight-line stability and self-centering of the steering wheel. However, excessive positive caster can lead to heavier steering, especially at low speeds.
2. Can I adjust the caster angle myself?
In most modern vehicles, adjusting the caster angle requires specialised tools and knowledge. It’s best to have a professional mechanic perform a wheel alignment to ensure proper settings. Some older vehicles or those with adjustable suspension systems may allow for minor adjustments, but it’s important to consult a professional if you’re unsure.
3. How often should I check my caster angle?
It’s recommended to have your vehicle’s alignment checked every 6-12 months, or more frequently if you notice any changes in handling or tire wear. Factors such as hitting potholes or curbs can affect your vehicle’s alignment.
4. What are the signs of excessive caster angle?
Signs of excessive caster angle can include:
- Uneven tyre wear: Excessive positive or negative caster can lead to uneven tyre wear, particularly on the inner or outer edges.
- Poor steering feels: The steering wheel may feel heavy or light, or it may not return to the centre easily.
- Vehicle pulling to one side: Excessive caster angle can cause the vehicle to pull to one side, especially at highway speeds.
- Reduced fuel economy: Uneven tyre wear caused by incorrect camber angles can increase rolling resistance, leading to reduced fuel economy.
5. Does caster angle affect fuel economy?
Yes, caster angle can indirectly affect fuel economy. Proper wheel alignment, including correct caster angles, can optimise tyre contact with the road, reducing rolling resistance and improving fuel efficiency. However, excessive caster angle can lead to increased tyre wear, which can negatively impact fuel economy.
6. What is the relationship between camber angle and toe angle?
Both camber angle and toe angle are important components of wheel alignment. Camber angle affects the vertical angle of the wheel, while the angle affects the horizontal alignment of the wheels. Both angles work together to influence a vehicle’s handling, stability, and tyre wear.
7. How does caster angle affect tyre wear?
Incorrect caster angle can lead to uneven tyre wear. The excessive positive or negative caster can cause accelerated wear on the inner or outer edges of the tyres, respectively.
8. Can a misaligned wheel affect fuel economy?
Yes, a misaligned wheel, including an incorrect camber angle, can negatively impact fuel economy. Misaligned wheels can increase rolling resistance, which requires more energy to overcome, leading to higher fuel consumption.
Conclusion
Camber angle is a crucial factor influencing a vehicle’s handling, stability, and tyre wear. By understanding the principles of camber angle, you can appreciate its impact on your driving experience.
While a positive caster angle generally improves straight-line stability and self-centering, excessive amounts can lead to heavier steering. Negative caster, on the other hand, can enhance responsiveness but may compromise stability.
To ensure optimal vehicle performance and tyre life, it’s essential to maintain proper wheel alignment, including correct camber angles. Regular vehicle inspections and professional wheel alignments can help keep your vehicle in top condition.
Affordable Adventures: Alpha Car Hire
Explore Australia with Alpha Car Hire’s budget-friendly car rental options. Whether you’re planning a city getaway or a long road trip, we’ve got you covered. Enjoy the freedom of the open road without breaking the bank.
Book your next adventure today!
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1727246131169{padding-top: 40px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_raw_html]JTVCcG9kcyUyMG5hbWUlM0QlMjJjYXJfaGlyZV9sb2NhdGlvbnMlMjIlNUQlN0IlNDBjYXJfaGlyZV9sb2NhdGlvbnMlN0QlNUIlMkZwb2RzJTVE[/vc_raw_html][/vc_column][/vc_row]
