A Parking Assistance System is a technology built into cars to make parking maneuvers easier and safer. It uses a combination of sensors, cameras, and software to provide information and guidance to the driver. Here’s a breakdown:
- Sensors: These are usually ultrasonic sensors mounted on the bumpers. They detect obstacles around the car and send that information to the system.
- Cameras: Rearview cameras are common, providing a live video feed of what’s behind the car. Some systems might use additional cameras for a 360-degree view.
- Software: This is the brain of the system. It processes the information from the sensors and cameras, calculates the best parking path, and displays warnings or guides the driver.
There are different types of Parking Assistance Systems, each offering varying levels of assistance:
- Basic Systems: These include rearview cameras and sensor alerts to warn you of obstacles.
- Advanced Systems: These can take more control over the steering, guiding the driver through the parking maneuver.
- Self-Parking Systems: The most advanced option, these systems can completely handle parking the car with minimal driver input
Why are they so important?
Think of all the benefits:
- Safety first: Parking assistance systems can significantly reduce the risk of accidents by detecting obstacles and blind spots you might not see. No more dings and dents!
- Stress less, park more: Maneuvering into tight spaces becomes a breeze. These systems take the guesswork out of parking, leaving you feeling calm and confident.
- Accessibility for all: Drivers with limited mobility can find parking assistance systems incredibly helpful. They make the entire process smoother and less physically demanding.
Types of Parking Assistance Systems
Parking assistance systems come in a variety of configurations, each offering a different level of sophistication and assistance. Let’s delve into the most common types:
1. Basic Parking Sensors
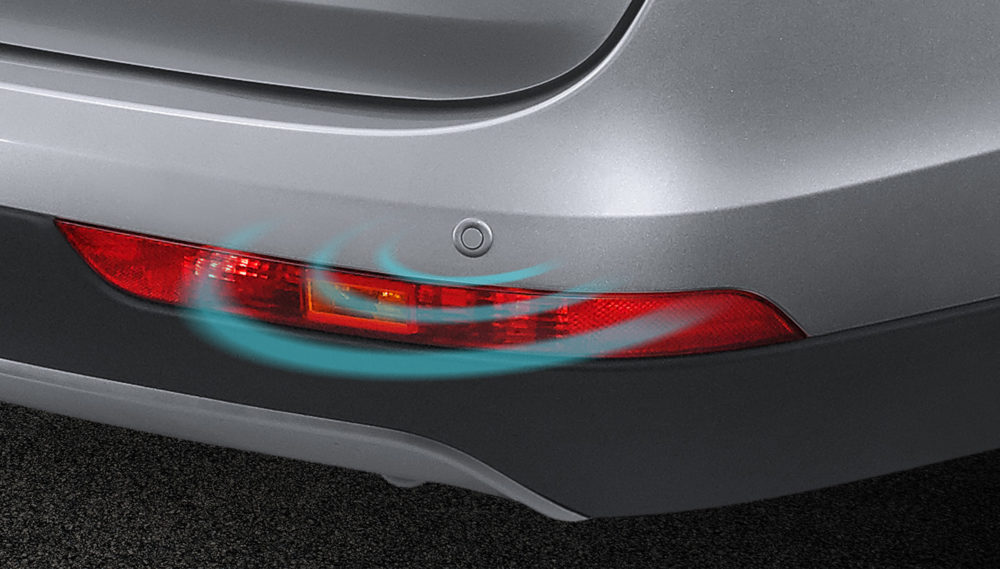

These are the workhorses of parking assistance, using sensors mounted on the front and rear bumpers to detect obstacles. There are two main types:
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These emit high-frequency sound waves and measure the time it takes for the echo to return. Based on the time difference, the system calculates the distance to an obstacle. As you get closer, the system emits a beeping sound that becomes more frequent as the distance decreases.
- Electromagnetic Sensors: These sensors detect changes in the magnetic field caused by nearby metal objects. They are less common than ultrasonic sensors and may be affected by other metal objects in the environment.
2. Rearview Cameras
Rearview cameras offer a real-time video feed of the area directly behind the vehicle. This visual aid helps drivers see obstacles that might be hidden from view, such as low objects or curbs. Many rearview camera systems also include superimposed guidelines that dynamically adjust based on the steering wheel position, helping you line up the car perfectly when parking in reverse.
3. Surround View Systems
system stitches the video feeds together to create a virtual 360-degree bird’s-eye view on the car’s display. This allows drivers to see all around the vehicle, eliminating blind spots and making tight maneuvering a breeze.
4. Automated Parking Systems
Components and Technology Behind the Magic
Parking assistance systems may seem like magic, but they rely on a clever combination of hardware and software working in perfect harmony. Let’s break down the key components:
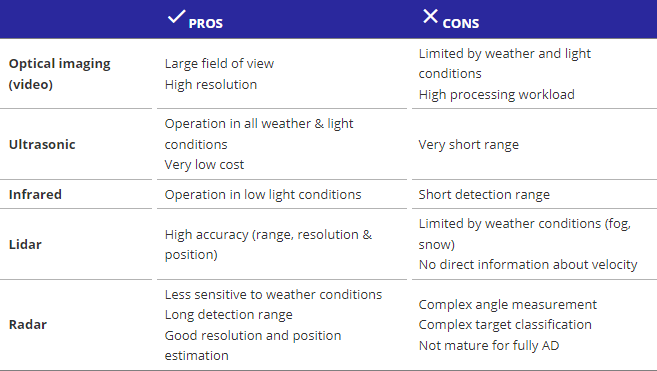
1. Sensors:
- Ultrasonic Sensors: As mentioned earlier, these emit sound waves and analyse the echoes to determine the distance to obstacles. They are reliable and relatively inexpensive, making them a popular choice.
- Radar Sensors: These emit radio waves and measure the reflected signal to calculate the distance and speed of nearby objects. They offer better performance in bad weather compared to ultrasonic sensors but are generally more expensive.
- LiDAR Sensors: These cutting-edge sensors use lasers to create a detailed 3D map of the surroundings. While expensive, they provide the most accurate and high-resolution data for complex maneuvers.
2. Cameras:
- Rearview Cameras: These standard cameras provide a live video feed of the area behind the vehicle.
- Surround View Cameras: Multiple cameras strategically placed around the car capture a panoramic view for a 360-degree perspective.
3. Electronic Control Unit (ECU):
This is the brain of the system. It receives data from all the sensors and cameras, processes it in real-time and makes decisions based on the software algorithms. The ECU then sends instructions to other systems in the car, such as the steering and brakes, to assist the driver or take control of automated parking systems.
4. Software:
The magic lies in the software that interprets the sensor and camera data. It uses complex algorithms to:
- Detect obstacles: The software identifies objects around the car and determines their size, position, and potential threat.
- Calculate parking maneuvers: Based on the available space and surrounding obstacles, the software calculates the optimal path for parking the car.
- Provide guidance: In basic systems, the software generates visual or audible alerts to warn the driver of obstacles. In advanced systems, it sends instructions to the ECU to control steering and braking during automated parking.
Functionality of Parking Assistance Systems
Now that we understand the different types and underlying technology, let’s delve into how these systems function to make parking a breeze:
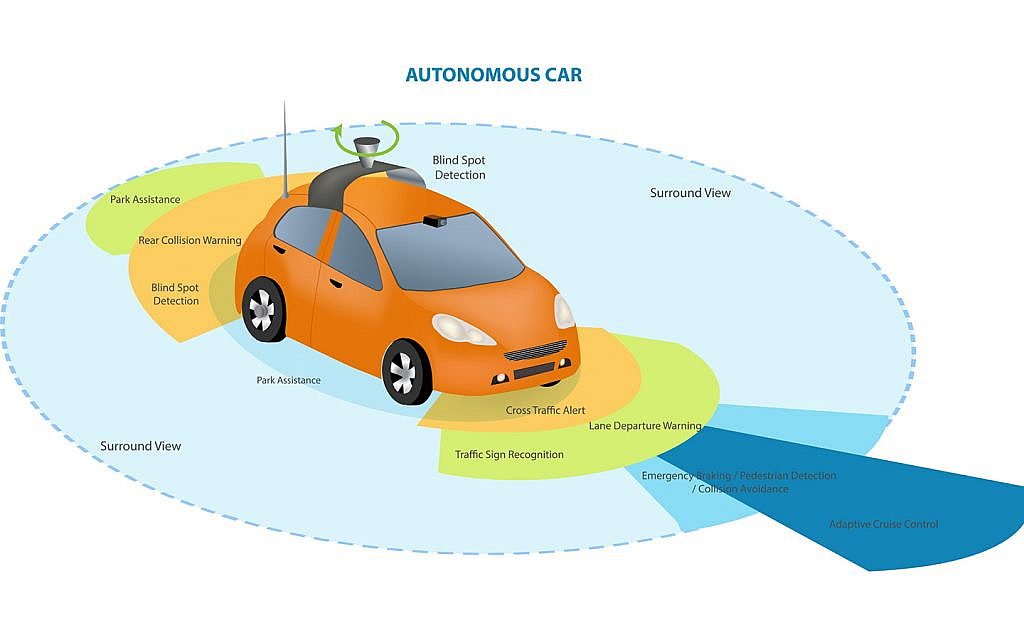
1. Detection of Obstacles
Parking assistance systems use a network of sensors to constantly scan the vehicle’s surroundings. The most common types are:
- Ultrasonic and Radar Sensors: These emit waves (sound or radio) and analyse the reflections to detect objects and calculate their distance. As you get closer, the system emits audible warnings (beeps) or visual alerts (lights) on the dashboard.
- LiDAR Sensors: These advanced sensors use lasers to create a detailed 3D map of the surroundings, providing the most precise obstacle detection.
2. Guidance and Steering Assistance
Basic systems offer visual guidance to help you park accurately. This can include:
- Rearview camera with dynamic guidelines: The camera overlays lines on the video feed that adjust based on your steering wheel position, helping you line up the car perfectly.
- Distance indicators: The system displays the distance to obstacles on the dashboard, allowing you to gauge how close you are.
Advanced systems take things further with steering assistance:
- Steering alerts: The system might gently nudge the steering wheel in the right direction to guide you into the parking spot.
- Partial steering control: Some systems can handle some of the steering tasks, requiring you to control the speed.
3. Automatic Parking
The ultimate in parking convenience, fully automated systems take over the entire parking process. Here’s how it works:
- Driver initiates parking: You activate the automated parking function and select the desired parking type (parallel, perpendicular).
- System scans for space: Sensors and cameras search for a suitable parking space based on your car’s size.
- Maneuvering the car: The system calculates the optimal parking path and controls the steering, braking, and acceleration to park the car autonomously.
- Driver confirmation (optional): Some systems might require you to confirm before engaging in certain maneuvers.
4. Integration with Other Systems
Parking assistance systems can interact with other vehicle features for a more comprehensive experience:
- Braking: Advanced systems can apply the brakes automatically to avoid collisions during parking maneuvers.
- Navigation: Some systems may integrate with navigation systems to suggest parking spots based on your destination.
The Many Benefits of Parking Assistance
Parking assistance systems offer a plethora of benefits that make driving life easier and safer:
1. Enhanced Safety
- Reduced risk of parking accidents by detecting obstacles and blind spots.
- Increased awareness of your surroundings, leading to safer parking maneuvers.
- Collision avoidance with automatic braking in advanced systems.
2. Convenience
- Stress-free parking, especially in tight spaces or busy parking lots.
- Less time is spent struggling to park, allowing you to focus on getting to your destination.
- Easier parking for drivers with limited mobility.
3. Damage Prevention
- Reduced risk of dings and scratches from parking mishaps.
- More precise parking leads to fewer accidental collisions with other vehicles or curbs.
4. Increased Parking Efficiency
- Automated parking systems can park cars more precisely, maximising available parking space.
- Faster parking maneuvers can improve traffic flow in crowded areas.
Overall, parking assistance systems are a valuable technology that can significantly improve the driving experience for everyone. From enhanced safety and convenience to reduced stress and damage, these systems are ushering in a new era of effortless parking.
Limitations and Considerations of Parking Assistance Systems
While incredibly helpful, parking assistance systems do have some limitations to keep in mind:
A. Reliability in Different Conditions
- Weather: Sensors can be affected by rain, snow, fog, or extreme temperatures. Performance might be reduced in these conditions.
- Lighting: Rearview cameras and some sensors may struggle in low-light situations.
B. Maintenance
- Sensor malfunction: Sensors can get dirty, damaged, or miscalibrated, requiring maintenance or replacement.
- Software updates: Systems might require software updates to maintain optimal performance.
C. Cost
- Advanced systems: Fully automated parking systems are typically found in high-end vehicles or as expensive add-ons.
- Retrofitting: Adding parking assistance systems to older cars might be possible but can be costly.
D. Dependency
- Over-reliance: Drivers shouldn’t rely solely on the system and should always remain vigilant and be prepared to take over if necessary.
- False positives/negatives: Systems might miss certain obstacles or give false warnings.
The Future of Parking Assistance is Bright
The world of parking assistance is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology:
1. Advancements in AI and Machine Learning
- Improved obstacle detection: AI can analyse sensor data more effectively to identify objects more accurately and in complex situations.
- Enhanced decision-making: Machine learning algorithms will allow systems to learn and adapt to different parking scenarios, improving overall performance.
2. Integration with Autonomous Vehicles
Parking assistance systems are a stepping stone towards fully autonomous vehicles. The technology developed for parking can be adapted to enable self-driving cars to navigate parking lots and maneuver into tight spaces seamlessly.
3. Smart City Infrastructure
Imagine a future where parking assistance systems communicate with smart city infrastructure. Parking spots could be pre-booked, and cars could automatically park themselves based on real-time availability and traffic flow.
Conclusion
Parking assistance systems offer a glimpse into the future of driving. By combining advanced technology with convenience and safety, these systems are revolutionising the way we park. As technology continues to develop, we can expect even smarter and more sophisticated parking solutions that make our roads safer and our parking experiences stress-free.
